
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Short Communication
- Technology/Device
- Comparison of Laser and Conventional Lancing Devices for Blood Glucose Measurement Conformance and Patient Satisfaction in Diabetes Mellitus
- Jung A Kim, Min Jeong Park, Eyun Song, Eun Roh, So Young Park, Da Young Lee, Jaeyoung Kim, Ji Hee Yu, Ji A Seo, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hye Jin Yoo, Nan Hee Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(6):936-940. Published online March 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0293
- 5,339 View
- 256 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Self-monitoring of capillary blood glucose is important for controlling diabetes. Recently, a laser lancing device (LMT-1000) that can collect capillary blood without skin puncture was developed. We enrolled 150 patients with type 1 or 2 diabetes mellitus. Blood sampling was performed on the same finger on each hand using the LMT-1000 or a conventional lancet. The primary outcome was correlation between glucose values using the LMT-1000 and that using a lancet. And we compared the pain and satisfaction of the procedures. The capillary blood sampling success rates with the LMT-1000 and lancet were 99.3% and 100%, respectively. There was a positive correlation (r=0.974, P<0.001) between mean blood glucose levels in the LMT-1000 (175.8±63.0 mg/dL) and conventional lancet samples (172.5±63.6 mg/dL). LMT-1000 reduced puncture pain by 75.0% and increased satisfaction by 80.0% compared to a lancet. We demonstrated considerable consistency in blood glucose measurements between samples from the LMT-1000 and a lancet, but improved satisfaction and clinically significant pain reduction were observed with the LMT-1000 compared to those with a lancet.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison between a laser-lancing device and automatic incision lancet for capillary blood sampling from the heel of newborn infants: a randomized feasibility trial
Chul Kyu Yun, Eui Kyung Choi, Hyung Jin Kim, Jaeyoung Kim, Byung Cheol Park, Kyuhee Park, Byung Min Choi
Journal of Perinatology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Comparison between a laser-lancing device and automatic incision lancet for capillary blood sampling from the heel of newborn infants: a randomized feasibility trial
Review
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Association between Variability of Metabolic Risk Factors and Cardiometabolic Outcomes
- Min Jeong Park, Kyung Mook Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):49-62. Published online January 27, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0316
- 5,714 View
- 221 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
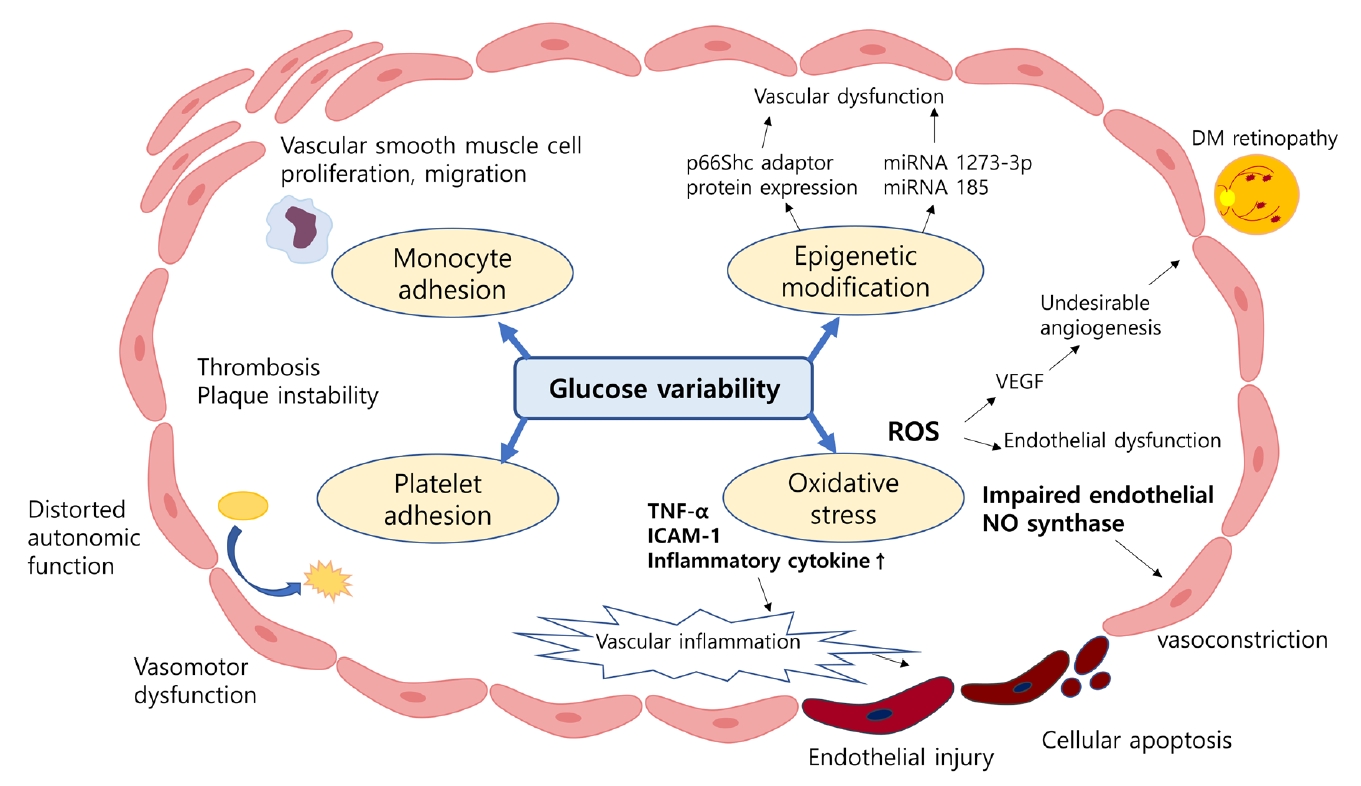
- Despite strenuous efforts to reduce cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk by improving cardiometabolic risk factors, such as glucose and cholesterol levels, and blood pressure, there is still residual risk even in patients reaching treatment targets. Recently, researchers have begun to focus on the variability of metabolic variables to remove residual risks. Several clinical trials and cohort studies have reported a relationship between the variability of metabolic parameters and CVDs. Herein, we review the literature regarding the effect of metabolic factor variability and CVD risk, and describe possible mechanisms and potential treatment perspectives for reducing cardiometabolic risk factor variability.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Long-term variability in physiological measures in relation to mortality and epigenetic aging: prospective studies in the USA and China
Hui Chen, Tianjing Zhou, Shaowei Wu, Yaying Cao, Geng Zong, Changzheng Yuan
BMC Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Dose–response relationship between physical activity and cardiometabolic risk in obese children and adolescents: A pre-post quasi-experimental study
Zekai Chen, Lin Zhu
Frontiers in Physiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of body weight change with all-cause and cause-specific mortality: A nationwide population-based study
So Yoon Kwon, Gyuri Kim, Jungkuk Lee, Jiyun Park, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 199: 110666. CrossRef - Association between lipid variability and the risk of mortality in cancer patients not receiving lipid-lowering agents
Seohyun Kim, Gyuri Kim, So Hyun Cho, Rosa Oh, Ji Yoon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between visit-to-visit lipid variability and risk of ischemic heart disease: a cohort study in China
Yonghao Wu, Peng Shen, Lisha Xu, Zongming Yang, Yexiang Sun, Luhua Yu, Zhanghang Zhu, Tiezheng Li, Dan Luo, Hongbo Lin, Liming Shui, Mengling Tang, Mingjuan Jin, Kun Chen, Jianbing Wang
Endocrine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Variability of Metabolic Risk Factors: Causative Factor or Epiphenomenon?
Hye Jin Yoo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 257. CrossRef - Long-Term Variability in Physiological Measures in Relation to Mortality and Epigenetic Aging: Prospective Studies in the US and China
Hui Chen, Tianjing Zhou, Shaowei Wu, Yaying Cao, Geng Zong, Changzheng Yuan
SSRN Electronic Journal .2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Long-term variability in physiological measures in relation to mortality and epigenetic aging: prospective studies in the USA and China

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





